Amazon Bedrock Guardrails enable you to implement safeguards and enforce responsible AI policies for your generative AI applications, tailored to specific use cases. With Guardrails, you create multiple tailored configurations and apply them across different foundation models, ensuring a consistent user experience and standardized safety controls across all your generative AI applications.
Guardrails allow you to configure denied topics to prevent undesirable subjects from being discussed and content filters to block harmful content in both input prompts and model responses. Guardrails can be used with text-only foundation models.
A guardrail consists of the following policies to avoid content that falls into undesirable or harmful categories:
- Denied topics: Define a set of topics that are undesirable for your application. These topics will be blocked if detected in user queries or model responses.
- Content filters: Adjust filter strengths to filter input prompts or model responses containing harmful content.
- Word filters: Configure filters to block undesirable words, phrases, and profanity.
- Sensitive information filters: Block or mask personally identifiable information (PII) and use regular expressions to define and then block or mask patterns that might correspond to sensitive information. Additionally, you can configure messages to be returned to the user if a user input or model response violates the guardrail’s policies.
Guardrails allows you to create multiple versions for iterative modifications. Start with a working draft, experiment with different configurations, and use the built-in test window to ensure they align with your use case. Once satisfied, create a version of the guardrail and use it with supported foundation models.
Guardrails can be applied directly to foundation models during inference API invocations by specifying the guardrail ID and version. If a guardrail is used, it will evaluate the input prompts and foundation model completions against the defined policies.
How to Create a Guardrail
- Navigate to the Amazon Bedrock console.
- From the left navigation menu, select Guardrails under Safeguards.
- Within the Guardrails section, click on Create guardrail.
- On the “Provide guardrail details” page, proceed as follows:
- In the “Guardrail details” section, enter a Name like bedrock-ws-guardrails and an optional Description for your guardrail.
- The Messaging for blocked prompts field allows you to set up the messages that you want to return to the user when the guardrail detects and blocks content. Enter the message to display if the guardrail blocks a prompt sent to the model. You can accept the default Sorry, the model cannot answer this question or enter you own message.
- Click “Next” to configure content filters.
Configure Content Filters
Guardrails supports content filters to detect and filter both harmful user inputs and FM-generated outputs. Content filtering depends on the confidence classification of user inputs and FM responses across each of the six harmful categories. All input and output statements are classified into one of four confidence levels (NONE, LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH) for each harmful category.
On the Configure content filters page, set up how strongly you want to filter out content related to the categories defined in Content filters by doing the following:
- To configure harmful category content filters, select Configure harmful categories filters. Configure how strict you want each filter to be for both prompts and responses. For this example, we will just accept the defaults.
- Select Configure prompt attacks filter. Accept the defaults.
- Choose Next.
Add Denied Topics
Let’s take the example, as a Fund Assistant Agent, the primary focus is to access data sources and provide accurate information to end users. In this use case, we want to avoid the system recommending a specific investment strategie.
For that, we are going to add a Denied Topic. On the Add denied topics page:
- To define a topic to block, choose Add denied topic.
- Enter a Name such as Property Investment Advice
- In the Definition for topic box, define the topic as “Property Investment Advice refers to giving recommendations to invest in property.
- (Optional) To add representative input prompts or model responses related to this topic, select the right arrow next to Add sample phrases. Enter a phrase such as “Should I invest in apartments in London?” then select Add phrase.
- When you’re done configuring the denied topic, choose Confirm.
- You can add more topics by choosing Add denied topic. For this example, we will proceed with one denied topic.
- When you are finished configuring denied topics, select Next.
Add Words Filters
Some of the funds available in our system invest in cryptocurrencies. So Go to the UI and ask: “Tell me the funds that invest in crypto.”
After the agents run and pull the info from our database, you will see a list of 2 funds:
- 21Shares Cardano ETP (AADA)
- 21Shares Ethereum Core ETP (ETHC)
Now we are going to configure a Words filter so we ensure we filter the questions when they mention these words. After we add this Guardrail to our agent, we will confirm that this question will be blocked.
Let’s create the word filter. On the Add word filters page:
- In the Filter profanity section, select Filter profanity to block profanity in prompts and responses. The profanity list is based on conventional definitions and is continually updated by Amazon.
- In the Add custom words and phrases section, you can select how to add words and phrases for the guardrail to block. There are 3 options:
- Add words and phrases manually
- Upload from a local file
- Upload from Amazon S3 object
For this example, choose option a: Add words and phrases manually. Add the following word filters:
- “crypto”
- “bitcoin”
- “cryptocurrencies”
Make sure to click on the check mark next to the word or phrase to accept the choice. When you are finished configuring word filters, select Next.
Add sensitive information filters
On the Add sensitive information filters page, configure filters to block or mask sensitive information.
- In the PII types section, configure the personally identifiable information (PII) categories to block or mask.
- To add a PII type, choose Add new PII. Then in the Type column, choose “Email”.
Guardrails can either “Block” or “Mask” responses based on the Guardrail behavior specified. For the Email, choose Mask as the behavior.
- Next, click on Add new PII, add an additional PII type for Credit/Debit card number. For the Guardrail behavior select Block.
- You can also add up to 10 regular expression patterns to filter for specific types of sensitive information and specify the desired guardrail behavior. You can leave this blank for the example.
- When you are finished configuring sensitive information filters, select Next.
Add contextual grounding check
Contextual grounding check evaluates for hallucinations across two paradigms:
Grounding — This checks whether the model response is factually accurate and grounded in the source. Any new information introduced in the response will be considered un-grounded.
- Set the Grounding score threshold to 0.85
Relevance — This checks if the model response is relevant to the user query.
- Set the Relevance score threshold to 0.5
- Select Next.
- On the Review and create page, check the configuration and details of your guardrail. Select Edit in any section that you need to modify. When you are satisfied, select Create guardrail.
Test the Guardrail
- Choose Guardrails from the left navigation pane. Then, select the guardrail you created from the Guardrails section.
- A test window appears on the right. Select the working draft of the guardrail to test, then click Select model. Select Anthropic > Claude 3.5 Sonnet v1 for this test, then click Apply.
- Copy the following text and paste it under the Prompt textbox of the test window. Then click the Run button.
Please summarize the below call center transcript. Put the name, email and the customer ID to the top:
Agent: Welcome to ABC company. How can I help you today?
Customer: I want to cancel my hotel booking.
Agent: Sure, I can help you with the cancellation. Can you please provide your customer ID?
Customer: Yes, my customer Id is trx-1234.
Agent: Thank you. Can I have your name and email for confirmation?
Customer: My name is Jane Doe and my email is [email protected]
Agent: Thank you for confirming. I will go ahead and cancel your reservation.
Notice that the input prompt includes an email address. The foundation model responds with a summary that contains the email address. However when the final response is generated, the Guardrail kicks in and masks the email with {EMAIL}.
To view the topics or harmful categories in the prompt or response that were recognized and allowed through the filter or blocked by it, select View trace. In this case, it shows that the final response was Masked because of the presence of an email.
Try the same process with the following prompt. Notice that Customer Id has been replaced by a credit card number.
Please summarize the below call center transcript. Put the name, email and the credit card number to the top:
Agent: Welcome to ABC company. How can I help you today?
Customer: I want to cancel my hotel booking.
Agent: Sure, I can help you with the cancellation. Can you please provide your credit card number?
Customer: Yes, my credit card number is 446849xxxxx96703.
Agent: Thank you. Can I have your name and email for confirmation?
Customer: My name is Jane Doe and my email is [email protected]
Agent: Thank you for confirming. I will go ahead and cancel your reservation.
The user prompt itself is blocked and is not sent to the foundation model for response generation.
Following the steps above, repeat this test by changing the user prompt to hit the different conditions you had configured the guardrail for and see how the final response generation is impacted. For example, try asking for investment advice using Bitcoins.
Add guardrail to Agent
To add guardrails to the agent created earlier in the example, perform the following steps:
- Select Agents from the left navigation pane in the Amazon Bedrock console and choose the name of the Agent (asset-management-agent) that you want to edit.
- In the Agents details page click on Edit in Agent Builder.
- Edit Agent Builder. On the Agent Builder page, locate the Guardrails details section and click Edit.
4. In the Select guardrail dropdown, select the guardrail that you just created, then for Guardrail version select either the Working draft or the deployed version you created.
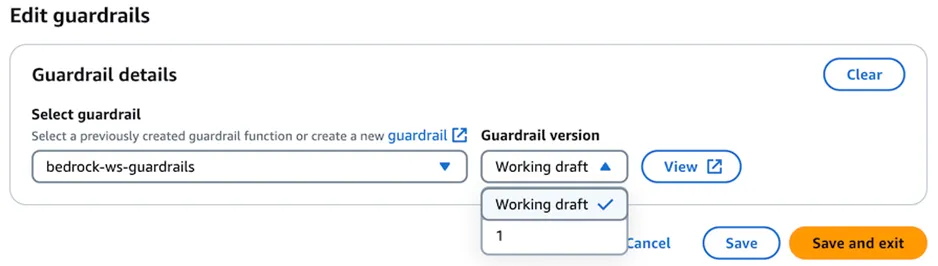
5. Select Save and exit to return to the Agent Builder page. You should see the guardrail added to your agent.
6. On the Agent Builder page, click Save and then Prepare and proceed to the next section to test the changes.
Test your Guardrail with Amazon Bedrock Agent
- To test the GFuardrail applied to the Agent, browse back to your UI.
- Ask the question:
which funds invest in crypto?
The agent will output:
Sorry, the model cannot answer this question.
Check the Traces, they will show detailed information regarding the reasons of the request being blocked.
Conclusion
Amazon Bedrock Guardrails provides safeguards that you can configure for your generative AI applications based on your use cases and responsible AI policies. You can create multiple guardrails tailored to different use cases and apply them across multiple foundation models (FMs), providing a consistent user experience and standardizing safety and privacy controls across generative AI applications. You can use guardrails for both model prompts and responses with natural language.

